Keeping a bass in a home fish tank can be a rewarding experience, allowing you to observe these fascinating creatures up close. However, ensuring the health and well-being of your bass requires meticulous attention to water quality. Bass are sensitive to changes in their environment, and maintaining proper water conditions is essential for their overall health and longevity. In this article, we’ll delve into the key aspects of water quality management for a bass tank and provide valuable tips on how to create a suitable habitat for these remarkable fish.
Amazon.com Water Testing Kit

1. Ammonia, Nitrite, and Nitrate Levels
One of the primary concerns in maintaining water quality is managing the levels of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate. Ammonia is released through fish waste and uneaten food, and its accumulation can be toxic to bass. Nitrite is a product of the breakdown of ammonia and is also harmful in elevated concentrations. Nitrate, a byproduct of the nitrite breakdown, is less toxic but can still be detrimental at high levels.
Tip: Regularly test the water using aquarium test kits to monitor these parameters. Keep ammonia and nitrite levels close to zero, and aim for nitrate levels below 40 ppm.
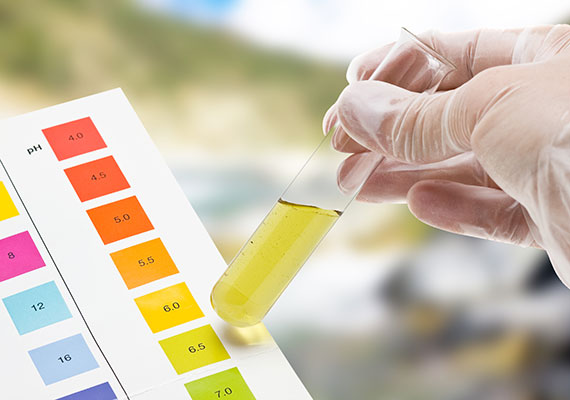

2. pH Balance
The pH level of the water greatly affects the health of your bass. Bass prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, usually between 6.5 and 7.5. Drastic fluctuations in pH can stress your fish and compromise their immune system.
Tip: Test the pH of your water regularly and consider using pH stabilizers if necessary. Avoid sudden changes in pH that can be caused by factors like adding untreated tap water.
3. Temperature Control
Bass are cold-blooded animals, meaning their body temperature adjusts to the surrounding water. Maintaining a stable water temperature is crucial, as rapid temperature changes can stress the fish and make them susceptible to diseases.
Tip: Invest in a reliable aquarium heater to maintain a consistent water temperature within the range of 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C), depending on the specific bass species.
4. Filtration and Aeration
A high-quality filtration system is essential to remove debris, excess food, and waste products from the water. Efficient filtration helps maintain water clarity and reduces the accumulation of harmful substances. Aeration, which increases oxygen levels in the water, is equally vital for bass health.
Tip: Choose a filter that is appropriate for the size of your tank and regularly clean or replace its filter media. Use an aquarium air pump to ensure proper aeration.
5. Regular Water Changes
No matter how advanced your filtration system is, regular water changes are essential to remove accumulated nitrates and other dissolved substances that can harm your bass.
Tip: Perform partial water changes of about 25% to 30% every 1-2 weeks. Use a dechlorinator when adding new water to neutralize any chlorine or chloramine present in tap water.
Sources:
- Raising Bass in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems – Auburn University (https://www.aces.edu/blog/topics/fisheries-aquaculture/raising-bass-in-recirculating-aquaculture-systems/)
- Bass: A Guide to Responsible Angling – The Bass Anglers’ Sportfishing Society (https://www.ukbass.com/bass-care-guide/)
- Water Quality for Freshwater Fish – Penn State Extension (https://extension.psu.edu/water-quality-for-freshwater-fish)
By diligently following these guidelines and regularly monitoring your bass tank’s water quality, you’ll create a thriving and vibrant environment that promotes the health and longevity of your prized bass. Remember that maintaining proper water conditions not only ensures the well-being of your fish but also enhances your enjoyment of this captivating hobby.